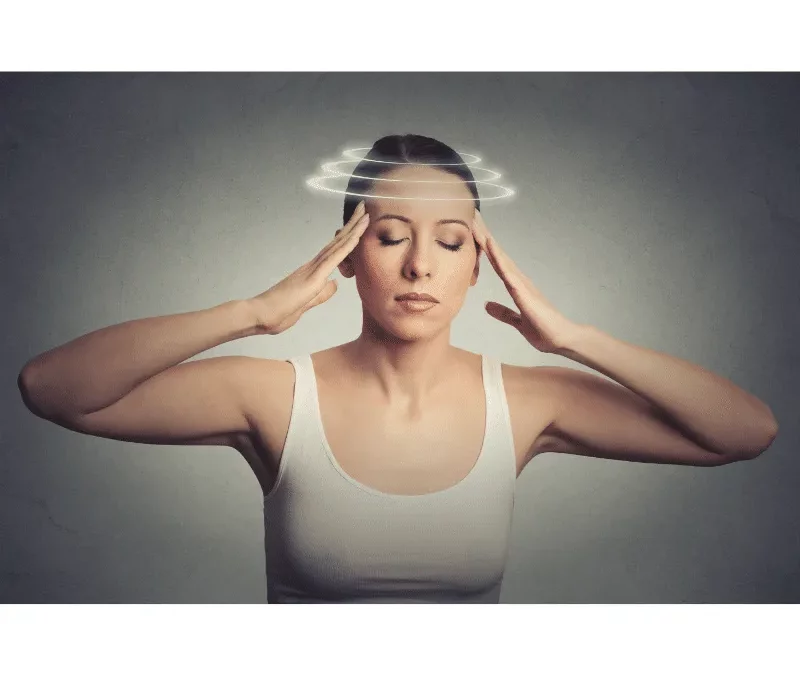
What is MDD
MAL DE DEBARQUEMENT (MDD) SYNDROME is a rare vestibular system disorder that is often described as feeling like you are on a boat while on land. Causes vary but risk factors include prolonged exposure on a boat, airplane, train or car. Other risks include being female and being between 40-50 years of age. The exact cause of MDD Syndrome is unknown, however studies have shown that a possible cause is related to the malfunction of the vestibular ocular reflex (VOR) which is a reflex in the inner ear that contributes to the ability to balance by stabilizing the eyes when the head is moving. MDD Syndrome occurs when the vestibular system is not able to readjust to a stable, non-moving surface after adjusting to a moving surface. For example, after a few days of being on a boat, your perception of the boat rocking decreases because the vestibular system has adapted, gaining “sea legs”. Similarly, once off the boat, the vestibular system has to readapt to a non-moving surface. MDD Syndrome can occur if the brain can’t readapt to prior movement. Other explanations include hormonal levels and vestibular migraines.
MAL DE DEBARQUEMENT (MDD) SYNDROME typically affects women with a correlation involving low estrogen levels. Reports have found symptoms worsen during the menstrual cycle and improve during pregnancy. In relation to migraines, MdDS symptoms are very similar to migraines (i.e. light sensitivity, nausea, etc.), leading some researchers to believe MDD Syndrome is a type of migraine.
How is MAL DE DEBARQUEMENT (MDD)SYNDROME diagnosed?
What are the most common symptoms of MAL DE DEBARQUEMENT (MDD) SYNDROME?
How long do symptoms last?
How can MDD be treated?
MDD Syndrome can be treated with vestibular rehabilitation therapy; training the vestibular ocular reflex to adapt to static land conditions. Training the vestibular system to respond to head movement has been effective in decreasing symptoms. When communication between the inner ear and brain is disrupted, awareness in space is altered, leading to feelings of unsteadiness. Symptoms may last from days to months; duration and intensity of symptoms have not been shown to correlate to the length of passive movement exposure.
Treatment involves training static and dynamic balance, visual fixation on a moving surface and a stable surface with head movement and habituation exercises to decrease sensitivity.
Medications have also been shown to be effective in decreasing symptoms of MDD Syndrome. Some of the more common medications used include Clonazepam and diazepam. Other avenues for treating MDD Syndrome include managing anxiety levels. Anxiety may potentially exacerbate symptoms.
Some exercises to try
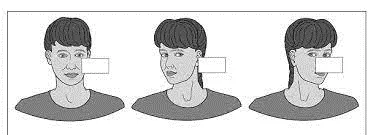
2. Eye tracking: Try staring at a small ball as you stand from a chair.

What does the research say about MDD?

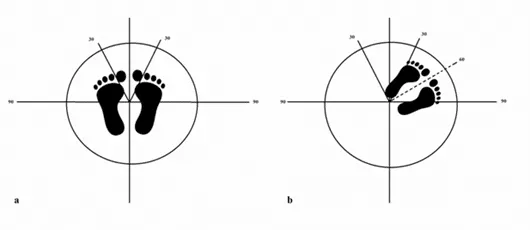
A more recent study compared the effectiveness of optokinetic cabins and the virtual reality application in terms of treatment of MDD Syndrome. The treatment group for optokinetic cabins were placed in a cabin similar to the picture above with moving stripes in 4 directions: left, right, up and down. The direction of the stripes is important as each person responds differently; if the incorrect direction is chosen, symptoms may be exacerbated. Direction of the stripes were determined using the Fukuda Step test, which determines if there’s a side of weakness in the vestibular system. The test is performed by standing on a piece of tape with arms outstretched in front of you and marching in place for 50 to 100 steps with the eyes closed. Once the eyes are opened, a new piece of tape will be placed where the last step was taken and the angle will be measured. If 50 steps were taken, any degree greater than 30 indicates vestibular weakness; with 100 steps taken, an angle greater than 45 degrees indicates weakness towards the side deviated. WIth this information, stripes will be moving towards the stronger side, which is also the side opposite to the pull or deviation. If the patient reported sensations of walking on clouds, feeling light to being pulled backwards, upward stripes were used.

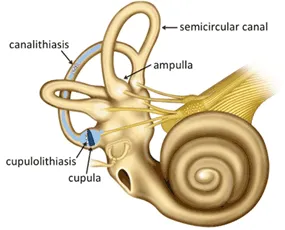
Other possible disorders
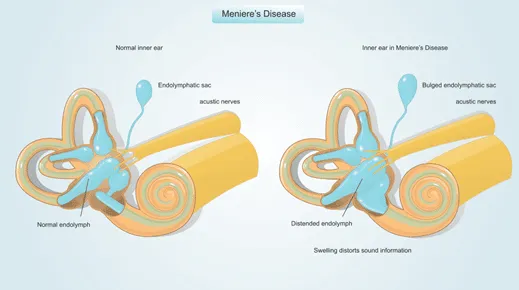
2. Meniere’s Disease is associated with fluid build up in the inner ear. Symptoms include vertigo, ringing in the ears, progressive hearing loss and feelings of fullness. Potential causes include viral infections, head trauma or damage to the drainage system.
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7461907/
https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2014/new-treatment-successful-for-rare-and-disabling-movement-disorder-the-mal-de-debarquement-syndrome-mdds
https://www.webmd.com/brain/mal-de-debarquement-syndrome
https://www.mddsreset.com/post/clinical-trial-started-in-antwerp-with-mdds-reset-vortex



